Audio Classifier with Edge Impulse
In this post you can find my second project on Edge Impulse with Arduino Tiny ML kit. I used audio dataset this time.
I would like to thank Coursera and Edge Impulse to give us a chance to learn embedded machine learning. Find more about the lecture: Coursera
In the project description two audio datasets are given, faucet and noise. I added blender audio to this dataset. I’ve run the blender for 2 minutes. Then using Audacity interface, I divided the 2 minute-data to 50 1-second data.
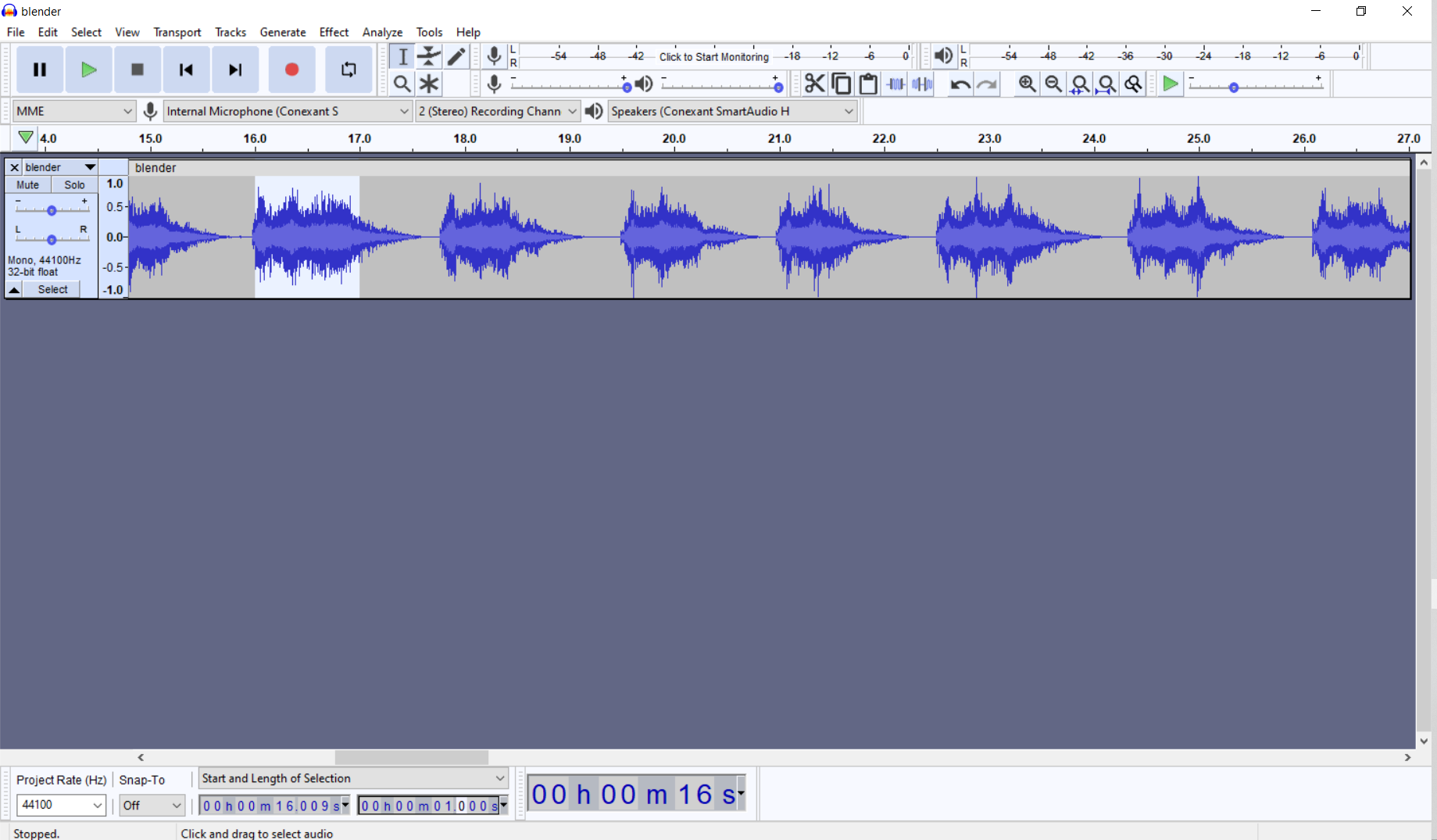
–
Rest of the steps are:
- Upload the data
- Create Impulse
- Generate Features
- Model Training
- Model Testing
I’ve tried two different feature extraction method. I will explain the details of them later in the post.
Deployment to Arduino
On the deployment page, select Arduino and click build. ei-audio_classifier-arduino-1.0.3.zip file is downloaded.
Since I didn’t collect the data with Arduino, this is the first time I connected Arduino to the computer.
Don’t forget to update the firmware: run flash_windows. After the firmware is updated open the command prompt:
$edge-impulse-daemon --clean.
I reentered my credentials and selected my current project.
Smile :)
[WS ] Device "myarduino" is now connected to project "audio_classifier"
[WS ] Go to https://studio.edgeimpulse.com/studio/75736/acquisition/training to build your machine learning model!
Now it is time to use Arduino IDE. From Sketch -> Add Zip Library, select ei-audio_classifier-arduino-1.0.3.zip
Select File -> Examples –> audio-classifier-inferencing- nano_ble33_sense_microphone_continuous
Here comes the final step: I clicked “Upload” to compile and send the program to Arduino. Unfortunately, I got this error:
Error sample buffer overrun. Decrease the number of slices per model window (EI_CLASSIFIER_SLICES_PER_MODEL_WINDOW)
ERR: Failed to record audio...
I decreased the EI_CLASSIFIER_SLICES_PER_MODEL_WINDOW from 3 to 2 by applying the directions on the website. Read more about this problem from: edge_impulse
/**
* Define the number of slices per model window. E.g. a model window of 1000 ms
* with slices per model window set to 4. Results in a slice size of 250 ms.
* For more info: https://docs.edgeimpulse.com/docs/continuous-audio-sampling
*/
# define EI_CLASSIFIER_SLICES_PER_MODEL_WINDOW 2
:)
I run the blender, and the result is below :) That’s great!
Predictions (DSP: 165 ms., Classification: 253 ms., Anomaly: 0 ms.):
blender: 0.00000
faucet: 0.00000
noise: 0.99609
Predictions (DSP: 165 ms., Classification: 253 ms., Anomaly: 0 ms.):
blender: 0.00000
faucet: 0.00000
noise: 0.99609
Predictions (DSP: 165 ms., Classification: 253 ms., Anomaly: 0 ms.):
blender: 0.62695
faucet: 0.00000
noise: 0.37305
Predictions (DSP: 165 ms., Classification: 253 ms., Anomaly: 0 ms.):
blender: 0.94531
faucet: 0.00000
noise: 0.05469
Feature Extraction
I got better results with MFE Feature Extraction. I used 2d conv net for MFE, while I used 1DConv for MFFC.
MFCCs are commonly derived as follows:
- Take the Fourier transform of (a windowed excerpt of) a signal.
- Map the powers of the spectrum obtained above onto the mel scale, using triangular overlapping windows or alternatively, cosine overlapping windows.
- Take the logs of the powers at each of the mel frequencies.
- Take the discrete cosine transform of the list of mel log powers, as if it were a signal.
- The MFCCs are the amplitudes of the resulting spectrum. wikipedia
MFE:
The Mel-scale is a perceptual scale of pitches judged by listeners to be equal in distance from one another. The idea is to extract more features (more filter banks) in the lower frequencies, and less in the high frequencies, thus it performs well on sounds that can be distinguished by human ear. edge_impulse
–
–
–
–
Key Words
Tiny ML, Arduino, Edge Impulse, Audio, Classification